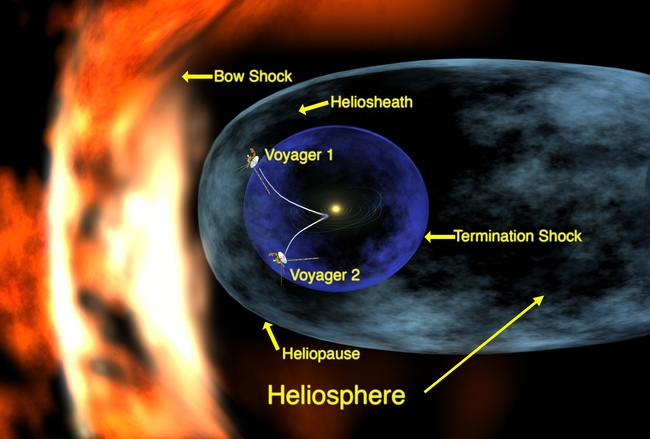
NASA’s Voyager 2 probe is approaching interstellar space and has detected an increase in cosmic rays that originate outside our solar system. Since 2007 it has been travelling through the outermost layer of the heliosphere.
Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets. Part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, Voyager 1, on a trajectory that took longer to reach Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with Uranus and Neptune.
The scientists of Voyager have been watching for the spacecraft to reach the outer boundary of the heliosphere. Once Voyager 2 exits the heliosphere, it will become the second human-made object, after Voyager 1, to enter interstellar space.
Voyager 2 is in a different location in the heliosheath (the outer region of the heliosphere) than Voyager 1 had been, and possible differences in these locations mean Voyager 2 may experience a different exit timeline than Voyager 1.
Ed Stone, Voyager Project Scientist said, “We’re seeing a change in the environment around Voyager 2, there’s no doubt about that, we’re going to learn a lot in the coming months, but we still don’t know when we’ll reach the heliopause. We’re not there yet that is one thing I can say with confidence.”
[source_without_link]SIASAT NEWS[/source_without_link]