Hyderabad: The Indian Pulsar Timing Array (InPTA) recently published its first official data release, critical for charting the interstellar ‘weather’ and paving the way to the discovery in the near future.
Prof Shantanu Desai from the Physics department of IIT Hyderabad, PhD student Aman Srivastava, B Tech student DivyanshKharbanda, and IITH alumnus RaghavGirgaonkar have co-authored this research article which got published recently in the publications of the ‘Astronomical Society of Australia’.
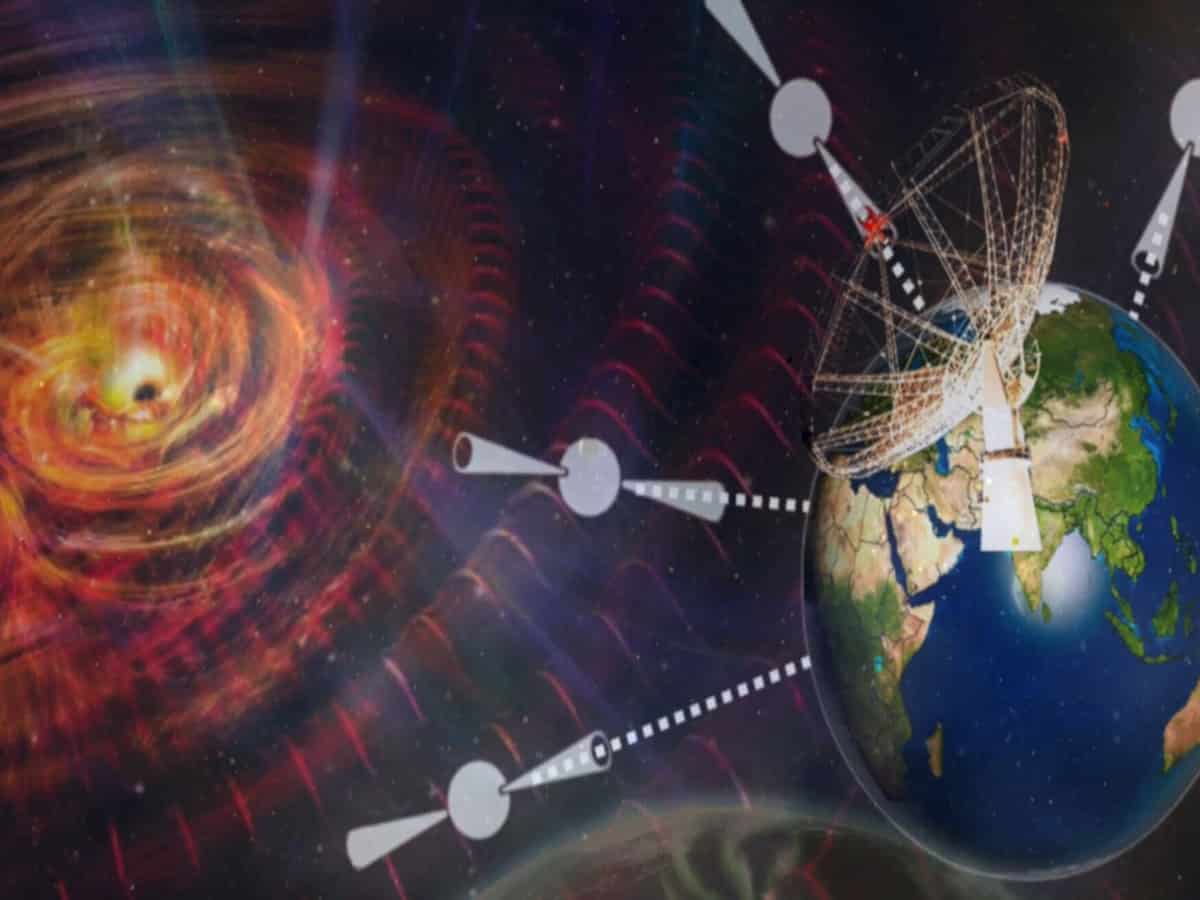
The data release stems from three and a half years of observation using the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) near Pune.
The Indo-Japanese team of thirty-eight radio-astronomers measures delays in the arrival of radio pulses from special types of neutron stars called millisecond pulsars, which are crucial for the discovery of low-frequency gravitational waves.
InPTA has joined hands with similar teams from the USA, Europe and Australia to detect these tiny, elusive ripples in spacetime, named nanohertz gravitational waves.
Director, IITH, Prof B S Murty, said “The InPTA collaboration involves both Indian and Japanese scientists working at multiple institutes and people at all levels (faculty, PhD students, postdocs, UG students, Engineers, Computing professionals etc.) who have actively contributed towards it.”
“This research helps us better understand our Universe and our role in it. However, one should remember wifi (ubiquitous) in daily life was a spin-off of research in radio astronomy while searching for radio bursts from primordial black holes,” added Prof Shantanu.
He also said, “The precision measurements which we are making use state of the art electronics and communication systems and also involve the application of novel data analysis and data mining tools. These could have potential industrial applications.”
The authors further explain that the universe is filled with gravitational wave background holding answers to deep secrets of nature. “The waves that we detect now are strong but short-lived. We are listening to large waves crashing loudly upon the seashore, whereas space-time is continually brimming with tiny ripples,” they said.
“Imagine a symphony where high-pitched sections blare at crescendos while bass sections play the fundamental progressions throughout. The interplay of gravitational waves in the universe is similar to a symphony played by nature,” briefed the author.
“We have been eavesdropping upon the crescendos while a persistent buzz forms the basis of this cosmic melody. These waves are generated by supermassive black hole binary pairs orbiting around each other for millions of years during their courses of collision. The primary hindrance in their detection is the vast ocean of interstellar medium lying in between,” added the author.



