
India has surpassed China in its population growth. The average life expectancy has also increased up to 70-75 years. More than 20% population of belongs to the age group of over 60 years.
Alzheimer’s disease or Alzheimer’s Dementia is a growing concern in elderly people. Currently 8.8 million people are living with Dementia in India. The number is expected to get doubled by the end of 2050.
Dementia is term used to describe a group of symptoms including loss of memory and other cognitive functions resulting in severe disability for person and emotional and financial burnout for caregivers.
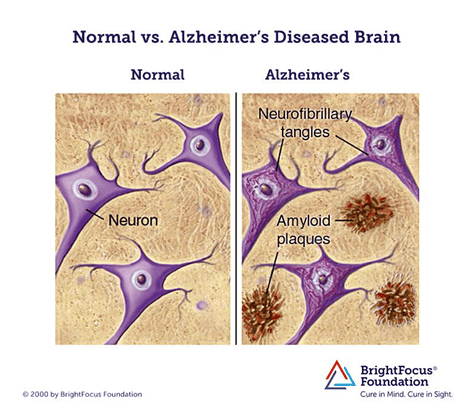
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of Dementia amounting to 60% of all Dementias. It is not just a part of aging process but it is a disease of brain wherein our brain cells are continuously dyeing (neurodegeneration) due to deposition of harmful proteins called ‘Amyloid plaques’ in brain cells i.e Neurons, resulting in loss of neuronal functioning.
Loss of memory is a primary symptom of Dementia but it is often associated with various other behavioural and psychological symptoms causing distress to person as well as the carers. Hence it is important to understand about this disease.
What are the warning signs of Dementia?
- Increasing memory loss
- Difficulty in performing familiar task like cooking, driving, managing accounts etc.
- Difficulty in communication i.e unable to articulate a sentence or find a proper word or repeating the same conversation
- Frequent disorientation in time and place, person might get confused between day and night or suddenly cannot recognise his own house and feels insecure.
- Frequently misplacing things and hence might feel that someone has stolen his things.
- Lack of judgment, decion making and problem solving and behaving inappropriately in social situations.
- Changes in personality, changes in mood and behaviour i.e a calm person might become an extrovert or a very active and social person can become dull and apathetic.
- Changes in sleep and appetite.
- Risk factors for Dementia
Alzheimer’s is commonly seen in old age i.e in persons who are more than 60-65 years but in some case it is also seen in <60 years which is called as early onset Alzheimer’s.
Females are at more risk of developing Alzheimer’s due to loss of protective effects of hormones with advancing age.
Apart from growing age common risk factors includes smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, uncontrolled hypertension and diabetes, lack of education, physical activities and socially engaging activities etc. Genetics (ApoE4 gene) play important role in causation and neuronal damage.
What is the course of this illness?
It is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. There is gradual and continuous decline in brain functions. Initially memory loss is limited to recent events such as forgetting about eating or taking medications and they might complain that they are not being fed on time, or forgetting a recent event such as wedding or attending an event etc. As the disease advances into middle or late stages remote memories are also lost. They cannot recognise even very close family members. Behavioural issues like agitation, restlessness, lack of sleep, anger spells, suspiciousness and hallucinations. Seeing and hearing unreal things become common. A person in advanced stages can forget how to eat, dress, take bath or going to toilet. He or she becomes more and more dependent for his activities of daily living (ADLs) on family members or caregivers. There is always risk of harm to self or others due to lack of judgment. Often, they wander outside home if left unsupervised and get lost. In very late stages they might become totally bedridden and need supportive and palliative care until the end of life.
How to diagnose Dementia?
If you are seeing these warning signs in your loved one, it is advisable to take advice of your doctor. Your family physician can do primary screening and refer you to a specialist like a neurologist or a psychiatrist. A specialist can do diagnostic tests which include some blood tests, memory & behavioural assessment. A brain scan especially MRI brain & PET scan can give more conclusive results.
Is there a cure for dementia?
There is no complete cure for dementia as it is a progressive Neurodegeneratingcondition. But there are medications to improve memory and cognitions thereby slowing the disease progression Medications can also help to improve sleep, minimize behavioural problems and minimise the distress. Apart from medications there are many behavioural and cognitive therapies to improve attention concentration, language and communication and reduce problematic behaviours.
These therapies can be given by trained Dementia care providers at different settings like Home, Day care centres or Respite carecentres. Family members can also learn these therapies and techniques.
Music therapies, art therapies and other recreational activities have promising role as well.
What can be done to prevent Alzheimer’s?
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Regular physical exercise, eating healthy food like vegetables and sea food, food rich in antioxidants and Flavonoids can delay the aging process.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Take adequate sleep and take meals on time.
- Challenge your brain with puzzles, sudoku, learning new skills and new languages.
- Keep check on your stress levels and anxiety issues.
Handling loved ones afflicted with Alzheimer’s
Understanding the disease is an important long-term strategy in caring for your loved one with Dementia. Keep in touch with your doctor and programmes that teach you about various stages and ways to cope and manage its symptoms
Keep a journal of their mental emotional and behavioural changes. This might help in determining next steps of management and making important decisions related to treatment, managing finances etc.
Caregiving for Dementia could be physically and emotionally stressful and exhausting. You must check on your emotional health as well. Time to time take advice from your doctors and attend regular support groups. Build a network of friends who are also in same role and try to learn healthy coping skills. Support groups and meeting are very useful in building resilience and improving the quality of life of you and your loved ones.
Dr Najamus Saquib is a senior psychiatrist who is associated with Asha Hospital located on Road Number 14, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad. drnajamussaquib@gmail.com
